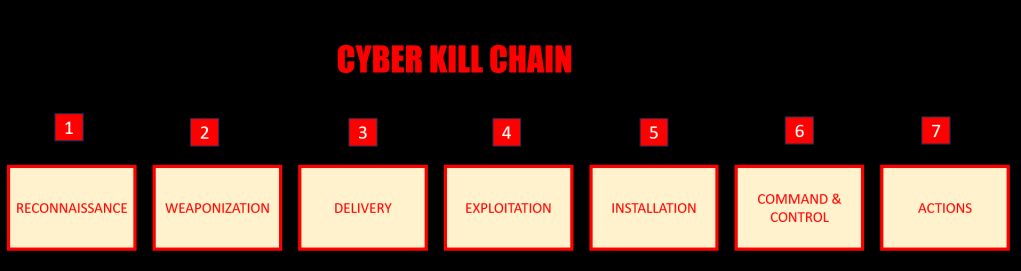
The Cyber Kill Chain is a concept in cybersecurity that describes the stages of a cyberattack, from the initial reconnaissance phase to the final objective, which is often data theft, system compromise, or other malicious actions. Developed by Lockheed Martin, the Cyber Kill Chain framework helps organizations understand and visualize the typical steps attackers take to achieve their goals. By analyzing and disrupting these stages, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity defenses. The Cyber Kill Chain typically consists of seven stages:
1. Reconnaissance:
In this initial stage, attackers gather information about their target. This might involve passive activities like searching the internet, scanning public websites, and social engineering to gather information about the target’s employees, systems, and vulnerabilities.
2. Weaponization:
After gathering information, attackers move to weaponization. They create or acquire malicious tools or payloads, such as malware, viruses, or exploit kits, designed to exploit specific vulnerabilities in the target’s systems.
3. Delivery:
In this stage, attackers deliver the weaponized payload to the target. Common delivery methods include phishing emails, malicious attachments, infected websites, or other means to get the malware onto the target’s network or system.
4. Exploitation:
Once the malicious payload is delivered and executed on the target’s system, the attacker exploits vulnerabilities to establish a foothold within the network. This stage often involves the exploitation of known software vulnerabilities or the use of zero-day exploits.
5. Installation:
After successful exploitation, the attacker installs backdoors, rootkits, or other malicious software on the compromised system. This allows them to maintain access and control over the victim’s network.
6. Command and Control (C2):
Attackers establish communication channels with the compromised systems to control and manage their malicious activities. They use these channels to send commands, exfiltrate data, and maintain persistence.
7. Actions on Objectives:
Finally, in the last stage, attackers carry out their primary objectives, which could include data theft, data manipulation, system disruption, or any other malicious actions they intended to achieve.
The Value of the Cyber Kill Chain:
Understanding the Cyber Kill Chain is valuable for several reasons:
- Threat Detection: By recognizing the stages of an attack, organizations can detect and respond to threats at various points in the chain, rather than waiting for an attack to reach its final stages.
- Risk Assessment: Analyzing the Kill Chain can help organizations identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their security posture, allowing for proactive risk mitigation.
- Incident Response: Understanding an attacker’s progression through the Kill Chain can inform incident response efforts, enabling organizations to disrupt attacks before they cause significant harm.
- Security Planning: The Kill Chain concept can guide the development of cybersecurity strategies and the selection of security technologies and practices to thwart potential threats.
It’s important to note that while the Cyber Kill Chain provides a valuable framework, not all attacks follow this linear path, and sophisticated adversaries may employ tactics to bypass or disrupt traditional defence mechanisms. Consequently, organizations often supplement the Kill Chain with additional cybersecurity models and strategies to create a comprehensive defence posture.
