The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework is a comprehensive set of guidelines, best practices, and standards designed to help organizations manage and improve their cybersecurity posture. NIST, part of the U.S. Department of Commerce, developed this framework to provide a structured approach to cybersecurity risk management. Here’s a detailed overview of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework:
1. Framework Core:
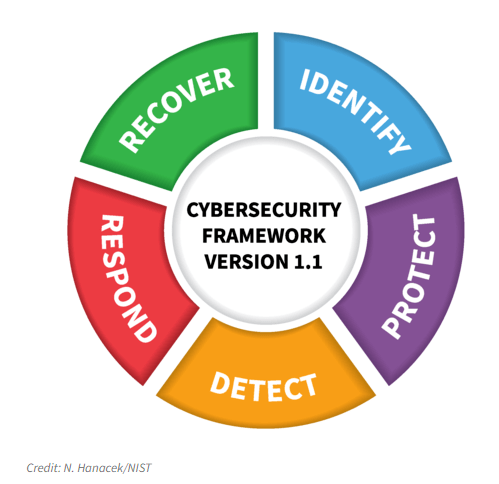
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework consists of three key components, with the “Framework Core” at its center. The Framework Core includes functions, categories, and subcategories that serve as the foundation for building and customizing an organization’s cybersecurity program:
- Functions: There are five core functions, each representing a high-level cybersecurity activity. These functions are Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. They form the backbone of the framework and provide a structured way to think about cybersecurity activities.
- Categories: Categories further break down the functions into more specific areas of focus. For example, within the “Protect” function, there are categories such as Access Control, Data Protection, and Awareness and Training.
- Subcategories: Subcategories provide granular guidance on specific actions and controls that organizations can implement to address cybersecurity risks. For instance, a subcategory might specify the use of multi-factor authentication for access control.
2. Framework Implementation Tiers:
The NIST framework defines four implementation tiers that reflect an organization’s cybersecurity risk management practices:
- Tier 1 – Partial: Organizations at this level have an ad-hoc approach to cybersecurity risk management, with limited awareness and minimal formal processes in place.
- Tier 2 – Risk Informed: Organizations at this level have a basic understanding of their cybersecurity risks and have started to develop more formalized processes and policies.
- Tier 3 – Repeatable: Organizations have a well-defined and repeatable approach to managing cybersecurity risks. They have policies and procedures in place, and they regularly review and update their cybersecurity practices.
- Tier 4 – Adaptive: Organizations at this level have a dynamic and adaptive approach to cybersecurity risk management. They continuously monitor and adjust their practices based on changes in the threat landscape and their specific needs.
3. Framework Profiles:
A Framework Profile is a representation of an organization’s current and desired cybersecurity posture. It involves selecting and customizing the framework’s functions, categories, and subcategories to align with the organization’s specific goals, risk tolerance, and resource constraints. Organizations can create different profiles to address different aspects of their cybersecurity program.
4. Framework Implementation:
Implementing the NIST Cybersecurity Framework involves the following steps:
- Prioritize and Scope: Identify critical assets, systems, and data that need protection and determine the scope of your cybersecurity program.
- Create a Current Profile: Assess your current cybersecurity practices and create a profile that reflects your existing posture.
- Set Target Profile(s): Define the desired cybersecurity posture(s) you want to achieve. These should align with your organization’s goals and risk tolerance.
- Identify and Implement Improvements: Identify gaps between the current and target profiles and develop plans to address them. Implement security controls and best practices accordingly.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor your cybersecurity program, assess its effectiveness, and make adjustments as necessary to adapt to changing threats and vulnerabilities.
5. Framework Use Cases:
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework can be used in various ways, including:
- Risk Management: It helps organizations identify, assess, and manage cybersecurity risks effectively.
- Communication: It provides a common language for discussing cybersecurity practices and risks within an organization and with external stakeholders.
- Compliance: It assists organizations in aligning with industry regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and others.
- Continuous Improvement: It supports ongoing assessment and improvement of an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is widely recognized and adopted by organizations around the world as a valuable tool for enhancing cybersecurity resilience and managing risks effectively. It provides a flexible and adaptable approach to cybersecurity, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes and industries.
